Recap of Chris Kuntz’s session at MD&M East 2025 on how AI copilots and AI agents are transforming manufacturing—from enhancing workforce capabilities to enabling autonomous operations.
At this year’s MD&M East, formerly IME East 2025, Augmentir took center stage as Chris Kuntz, VP of Strategic Operations, delivered a powerful presentation on the transformative role of AI Copilots and AI Agents in manufacturing.
Read below for a brief recap of the presentation, as well as a video recording of the presentation.
Addressing the Workforce Crisis with AI
Chris opened with a sobering reality: even if every skilled worker in the U.S. were employed, 35% more manufacturing jobs would remain unfilled. Citing a $1 trillion annual opportunity cost by 2030 (Deloitte), Chris emphasized that traditional workforce strategies aren’t enough—and the time for intelligent automation and workforce augmentation is now.
Key Highlights from the Presentation
The Rise of AI Copilots and AI Agents
Chris introduced AI Copilots as conversational tools powered by LLMs, providing contextual, real-time support to workers. AI Agents, on the other hand, are autonomous systems that execute complex tasks independently—reducing friction, downtime, and manual inefficiencies.
The Augmented Connected Worker
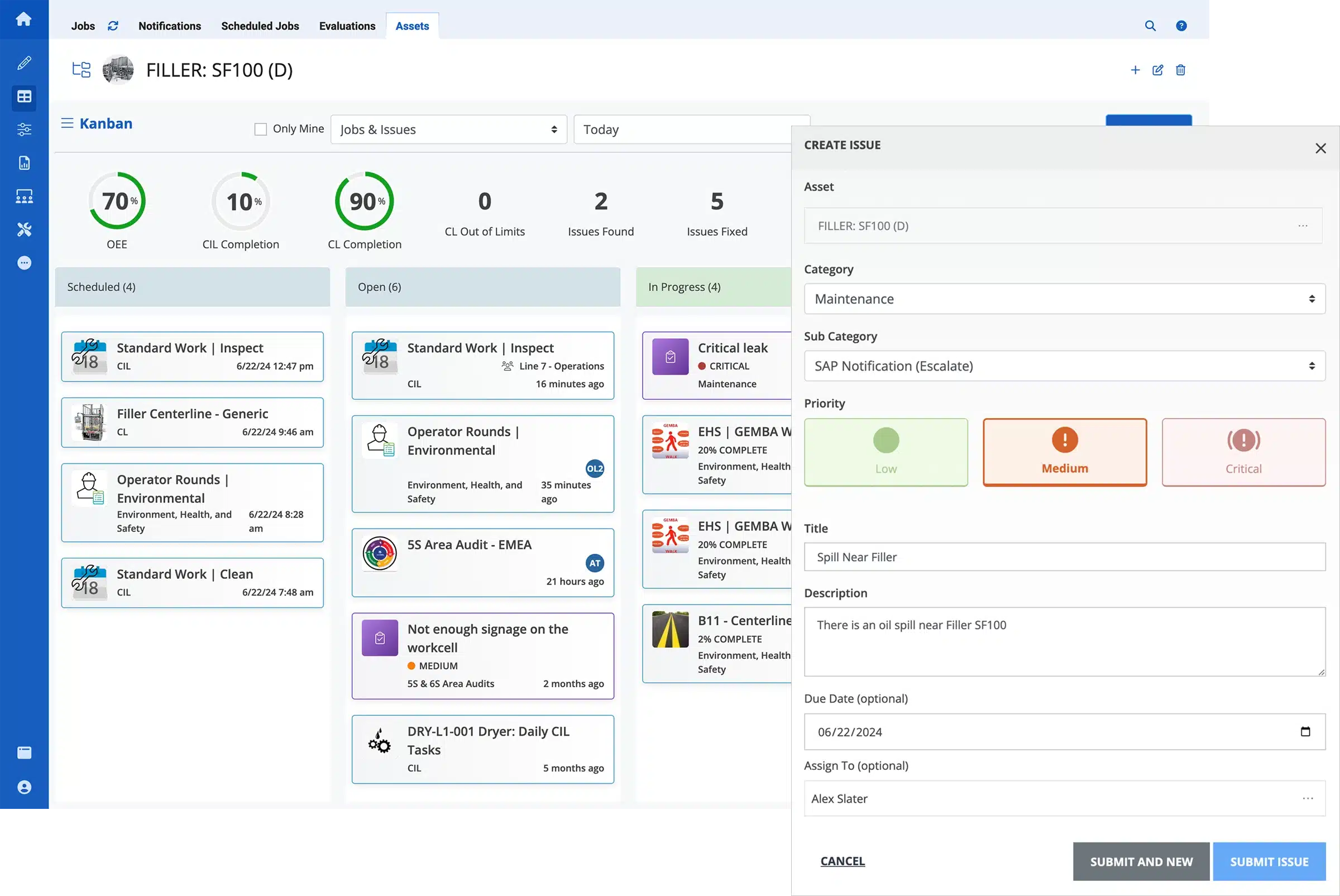
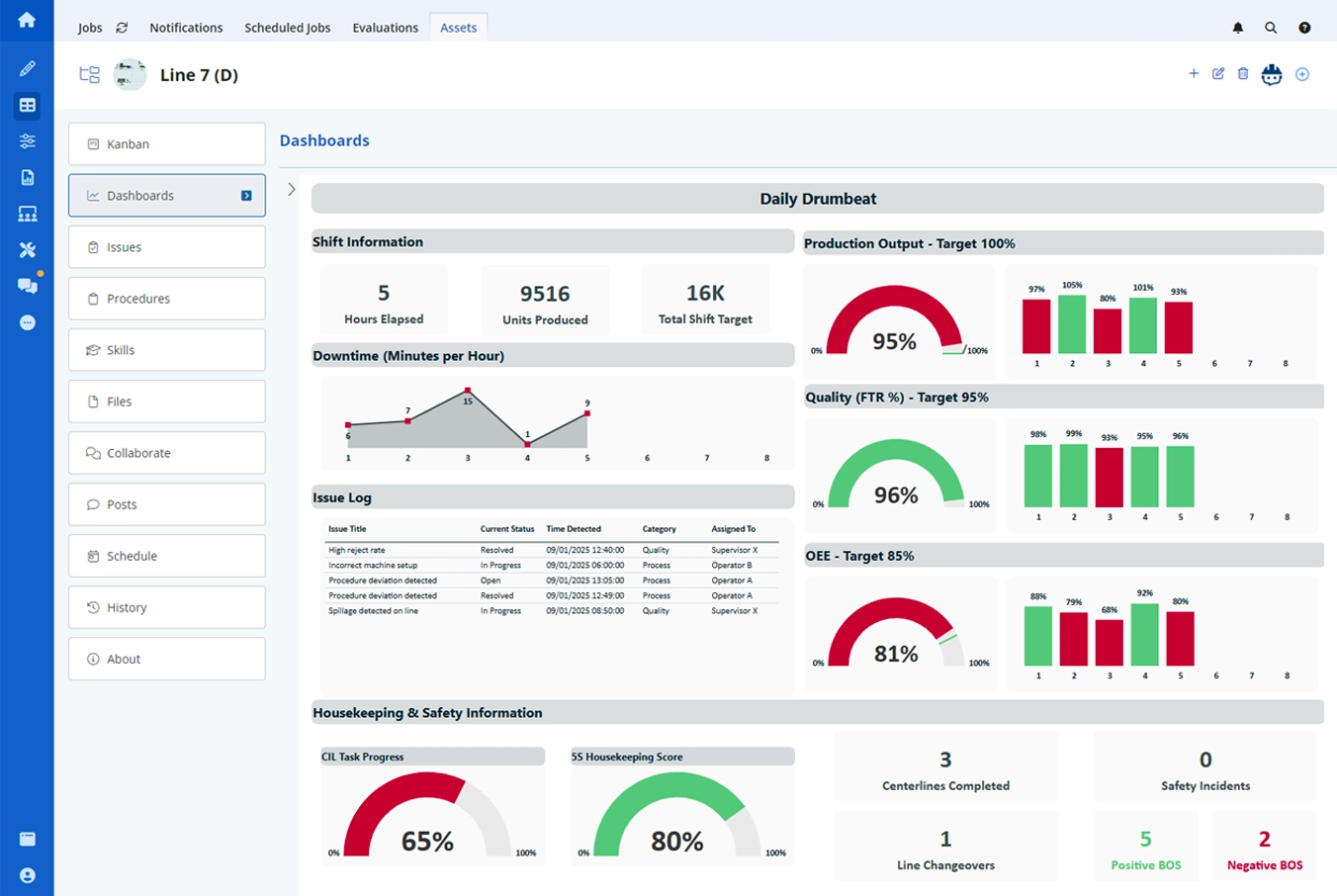
At the heart of the talk was Augmentir’s Connected Worker technology—a framework that brings together:
- AI-powered guidance and support to help frontline workers perform tasks more efficiently, safely, and accurately.
- Real-time data capture and insights that drive continuous improvement across operations, training, and workforce performance.
- A unified digital platform that connects people, processes, and systems to enable scalable workforce transformation in manufacturing.
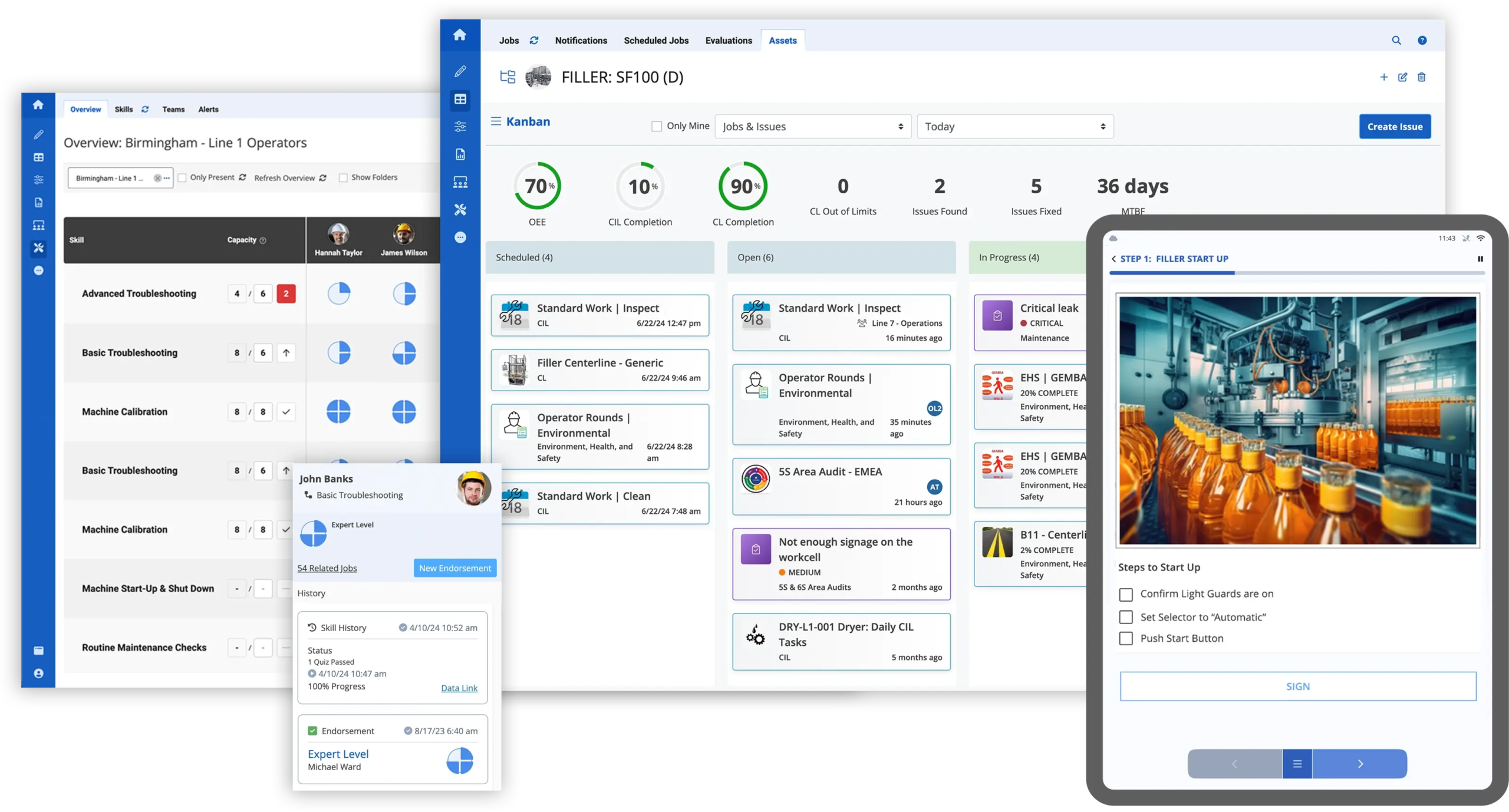
6 Game-Changing Use Cases
Chris walked attendees through six real-world use cases—showing how Augmentir and Augie are delivering measurable outcomes for manufacturers:
- Content Assistant – 76% faster digitization of SOPs and training docs
- Work & Training Assistant – 82% reduced onboarding time
- Image Comparison – Improved inspection accuracy, reduced rework
- Skills & Training AI Agent – On-demand learning and certification
- Operations Agent – Real-time troubleshooting support
- Corporate Knowledge Graphs – Smarter access to institutional knowledge
Case studies from leading packaging and beverage companies added real-world credibility, demonstrating how organizations are scaling faster while minimizing downtime and safety incidents.
Video Recording
Full Transcript
My name is Chris Kuntz. I’m with an AI company called Augmentir, and we provide connected worker software for frontline workers in manufacturing. Today what I’ll be talking about is artificial intelligence, which in many ways has taken over the media, and become a major part of our lives, but I want to talk about it in the context of manufacturing and specifically talk about generative AI assistants and AI agents that can be used in manufacturing to help guide and support today’s frontline workers.
So just a quick 30 seconds on Augmentir and who we are as a company. We’re a relatively young company, founded in 2018, but we have a pretty deep history in innovative software and manufacturing, dating back to the late 1980s. The founders of Augmentir were the same industry innovators that founded Wonderware in 1987, which revolutionized HMI software in factories. Wonderware went public and is now part of AVEVA/Schneider Electric. We were the founders of Lighthammer, which is now part of SAP’s MII offering. And we were the founders of ThingWorx, which is now part of PTC and revolutionized the Industrial Internet of Things space. And when we left PTC, the team got back together again and we wanted to focus on tackling what we considered to be the next big problem in manufacturing at the time, which was the human worker.
If you think about AI and how it’s been, automation and how AI has optimized production lines, really the last mile for driving efficiency in manufacturing is the human worker. And even more apparent over the past five years since the pandemic, the labor shortage, the skilled labor shortage has created dramatic impacts on product quality, product efficiency, and overall throughput in manufacturing. And so our goal at Augmentir was to tackle that.
So let’s start this conversation by talking about AI and the history of AI in manufacturing. And it dates back to the 1960s. AI has been used in automation in manufacturing for decades now. It’s been used to drive incredible levels of efficiency. It’s been used in machine vision systems for quality improvements. And you see that you, when you walk around, manufacturing trade shows like this, it’s been used in warehouse in warehousing automation, and more recently, it’s been used in the industrial internet of things, digitally connecting equipment and using AI to analyze the data that is coming off of that equipment to drive greater efficiencies in production, production efficiency in manufacturing. But a common theme across all of this is up to this point, AI has been used to replace the human worker or to optimize manual labor or manual efforts that humans were doing in factories, previously. AI has a unique opportunity, specifically around generative AI co-pilots, if you think ChatGPT or AI agents, is to augment the human worker, not replace them.
And so the question we asked ourselves at Augmentir, when we started, was, can AI do the same for humans? Can AI drive efficiency for the humans that are still on the shop floor in manufacturing, quality, engineering, and maintenance roles and in equipment operation. More importantly, in maintenance, can AI be used to optimize the work that they’re doing? And why now?Here are some statistics from a report that LNS Research, an analyst firm based out of Boston ran last year on the future of industrial work. Pretty fascinating statistics. When they look at the average tenure rate in manufacturing, 2019 compared to the end of last year. So from 20 years to three years, the average time and position went down from seven years to nine months, and the average three-month retention rate, the rate at which people stay in after the first three months, from 90% down to 50%. So the problem you have in manufacturing today is yes, there’s a labor shortage, yes, it is difficult to find skilled labor, but because humans are required in manufacturing, what organizations are doing is hiring less skilled workers. And now you have a problem that’s really twofold on the shop floor. You have less experienced workers that also have less experience or less skilled workers, also have less experience. And that results in safety issues, quality issues, product recalls, downtime, everything possible that you can imagine that relates to human error in or on a factory floor.
In this survey, from LNS, the respondents, 92% of them said they were looking at technology as a way to offset that skilled labor gap. Now, it’s not the only solution, certainly there are better hiring strategies, better training strategies, but certainly looking at technology as a big piece of offsetting that labor crisis. Just another statistic here from a study in Deloitte, even if every skilled worker, and this is just in America, even if every skilled worker was employed, there would still be a 35% gap in unfilled job openings in manufacturing. That’s how bad it is. And so Deloitte predicts by 2030, that it’s a $1 trillion problem in the US alone. And I think they forecasted $3 trillion globally, a problem that exists for production output and manufacturing.
So that brings us to what we’re talking about here today, AI agents and co-pilots. Everyone here has used ChatGPT or Gemini or Perplexity or whatever, chatbot you want to use today, fantastic results and fantastic opportunities when you think about consumer AI, but what I want to do is talk about the context of AI assistance, as well as agents, which there’s some blurring of the line there, but we’ll talk about that, and their applicability in industrial operations and why it’s quite a bit different from consumer AI.
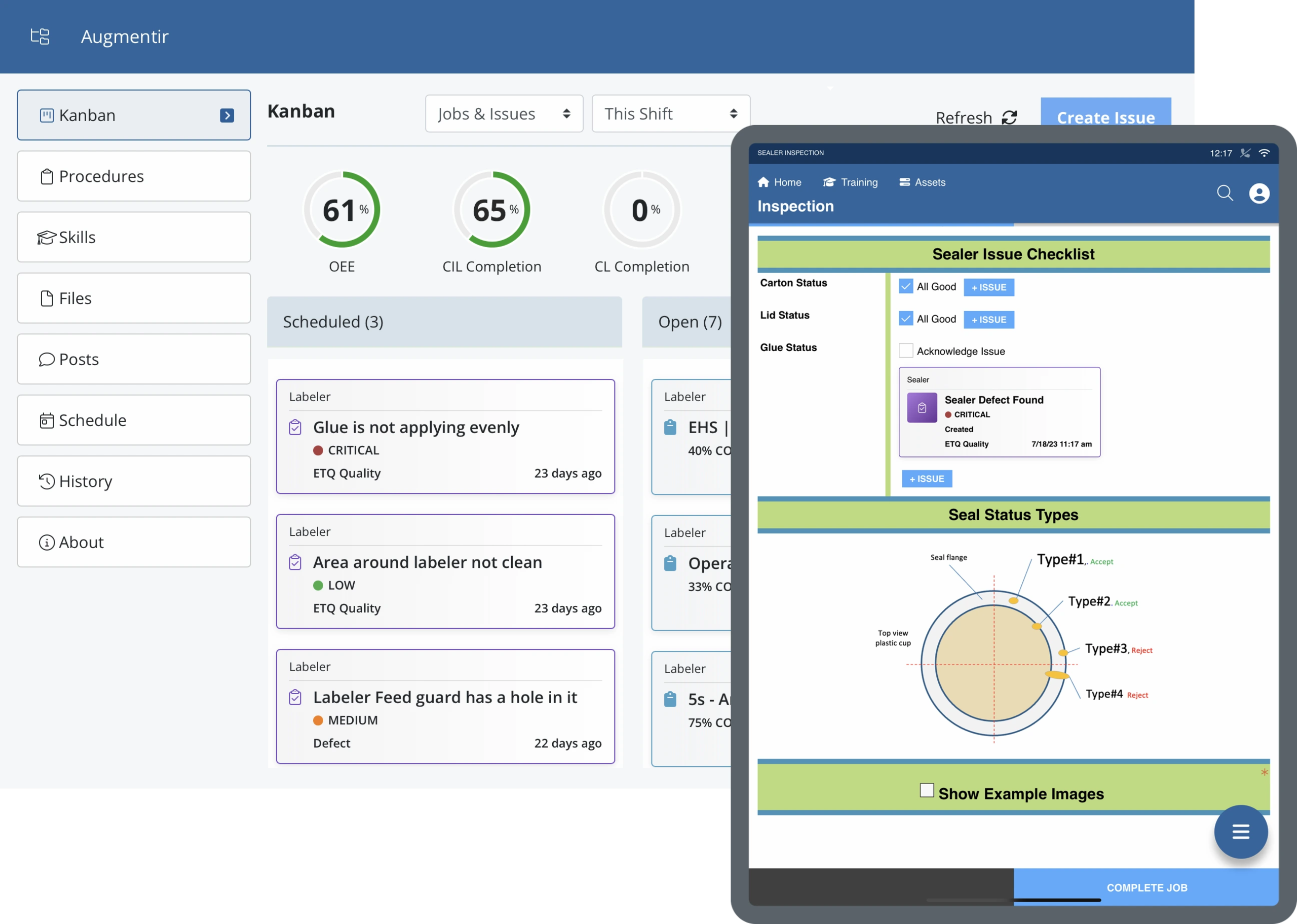
So what is an AI co-pilot? Best example is ChatGPT, right? We’ve all used it. Natural language interface, the ability to use what they call a large language model, LLM, for those of you that might not be as technical, which has the ability for that agent or that assistant to understand vast amounts of data and it provides context assistance to users. On the flip side, what is an agent? An agent is an AI bot that acts more autonomously. They can operate based on a prompt like you would have with ChatGPT, but they don’t have to. So they can actually take autonomous action based on instructions you give it. Now, when you think about it, I’m going to use ChatGPT as an example today because I think we’ve all probably used it or used something similar. They’re starting to blur the lines a little bit with their, I think they’re calling it the ChatGPT operator, so that’s starting to blur the lines between autonomous and strictly prompt-based AI. But the idea is the same in the context of today, what we’re talking about in terms of an AI co-pilot or an assistant that is a prompt-based bot that that a user might be using. And from an agent standpoint, it is something that can act more autonomously. And a prerequisite to all this, when you think about manufacturing and you think about frontline workers, whether they are working in safety, quality, equipment and machine maintenance and repair or equipment operation, a prerequisite to all this is the ability to have a connected worker.
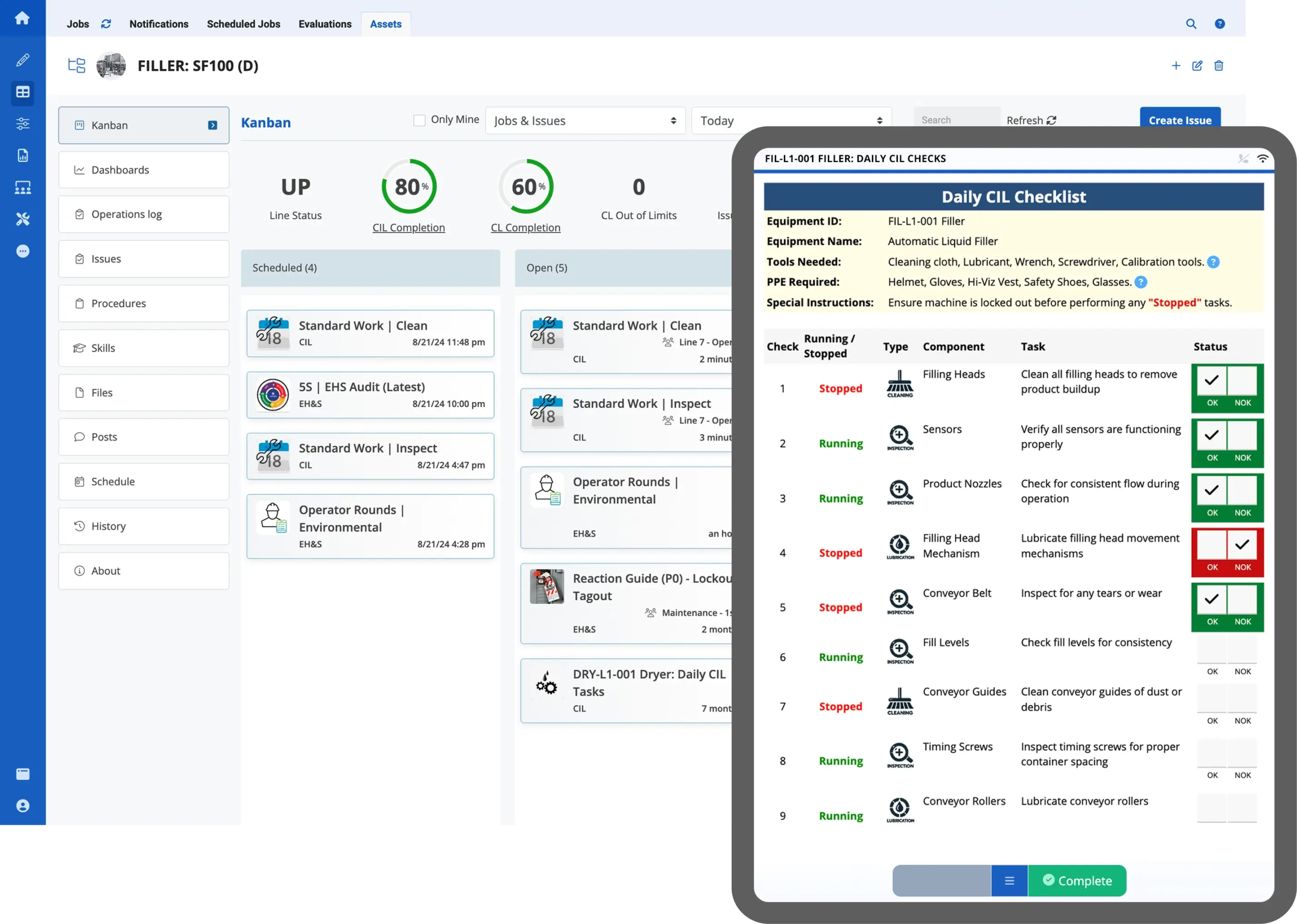
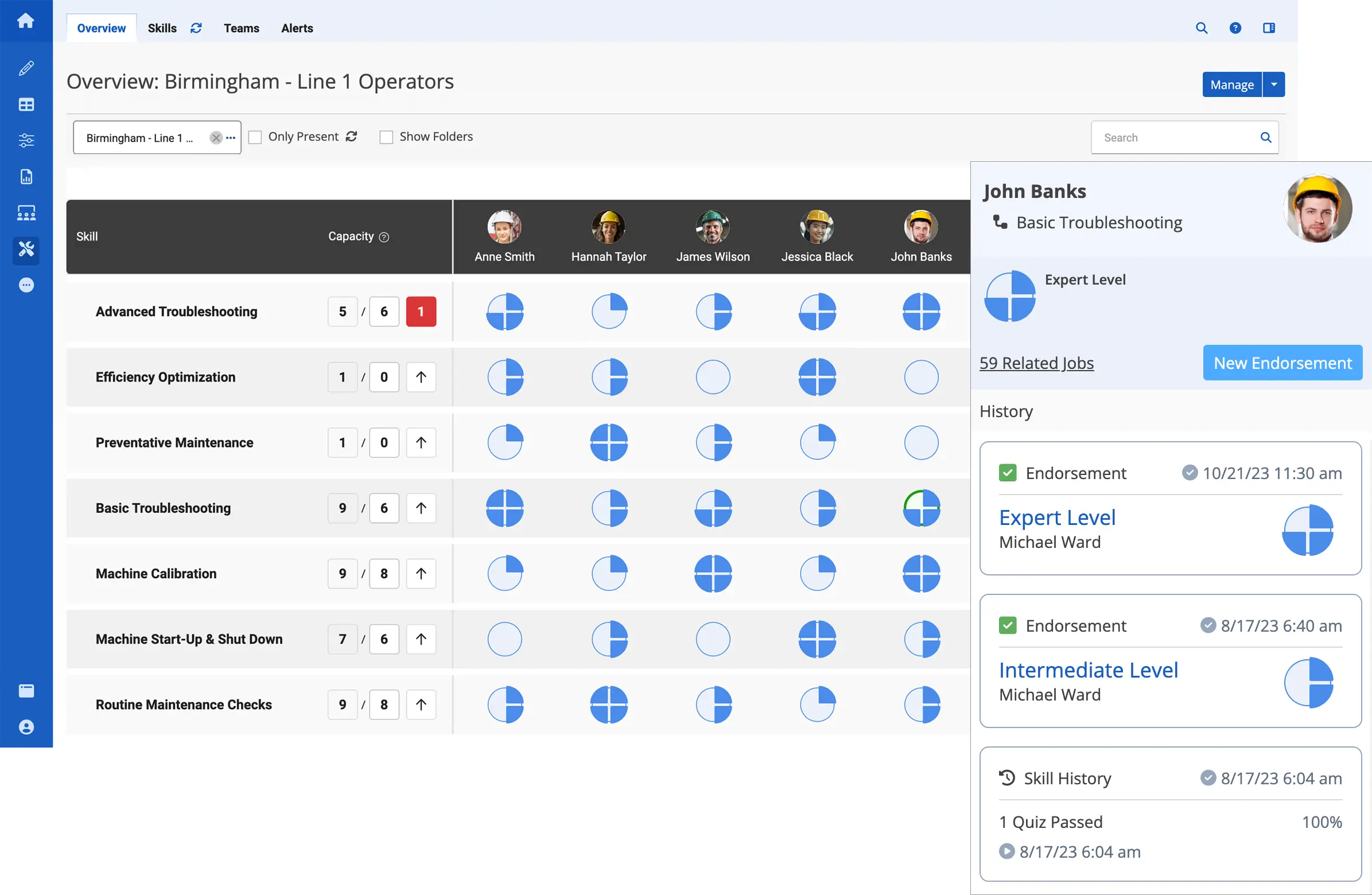
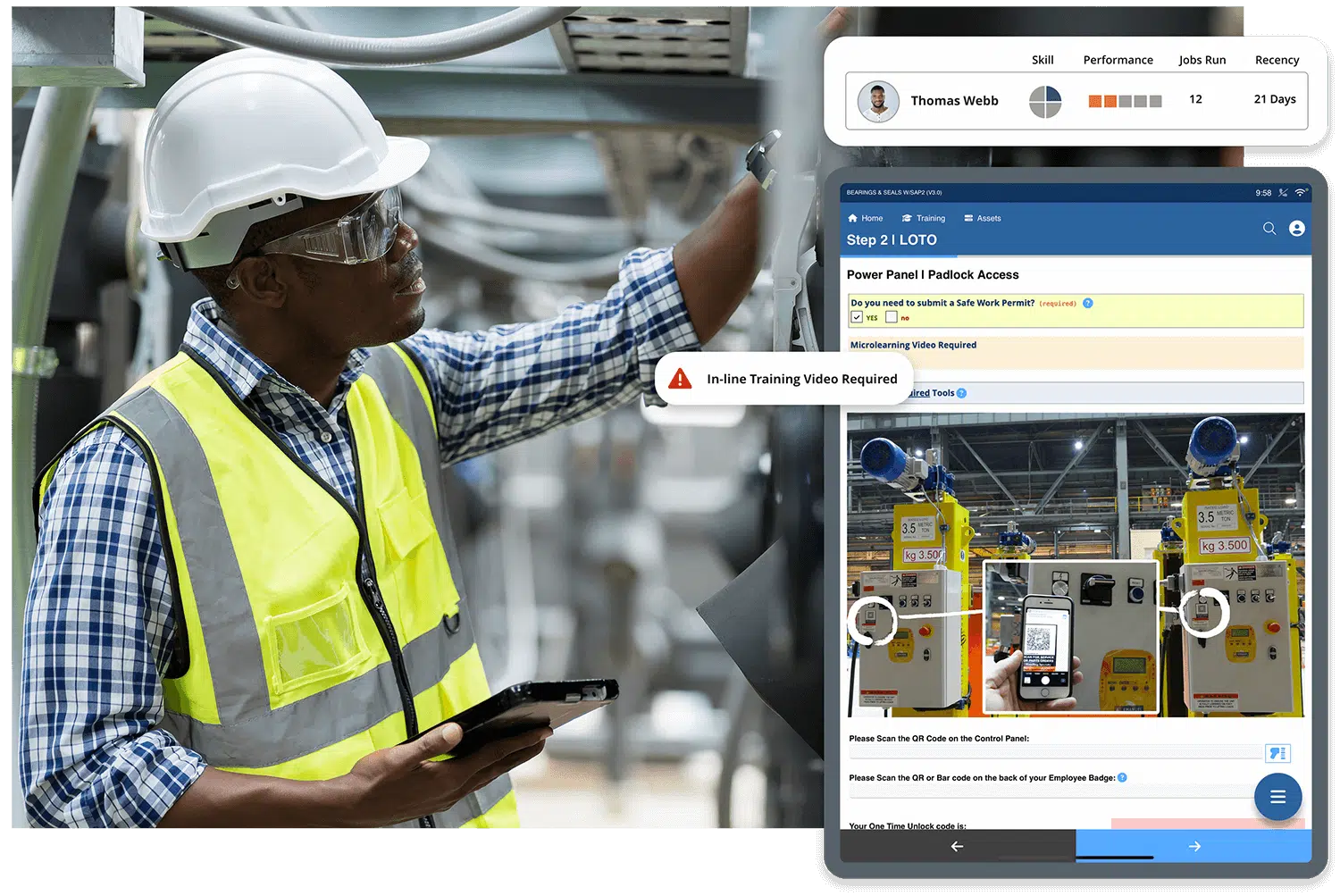
And by connected worker, what we like to talk about at Augmentir is a worker that is not only connected with a digital or a mobile tool, like a phone, a tablet, a wearable technology, a wearable augmented reality-based headset, for example, but also digitally connected into the business. So using that interface to not just connect them physically with a device, but connect them into HR systems, learning management systems, ERP systems, quality systems, and safety systems, systems that they use every day. But now that they’re connected, they can become human sensors on the shop floor. And there’s a vast amount of data that we can then capitalize on here, and AI can then act on.
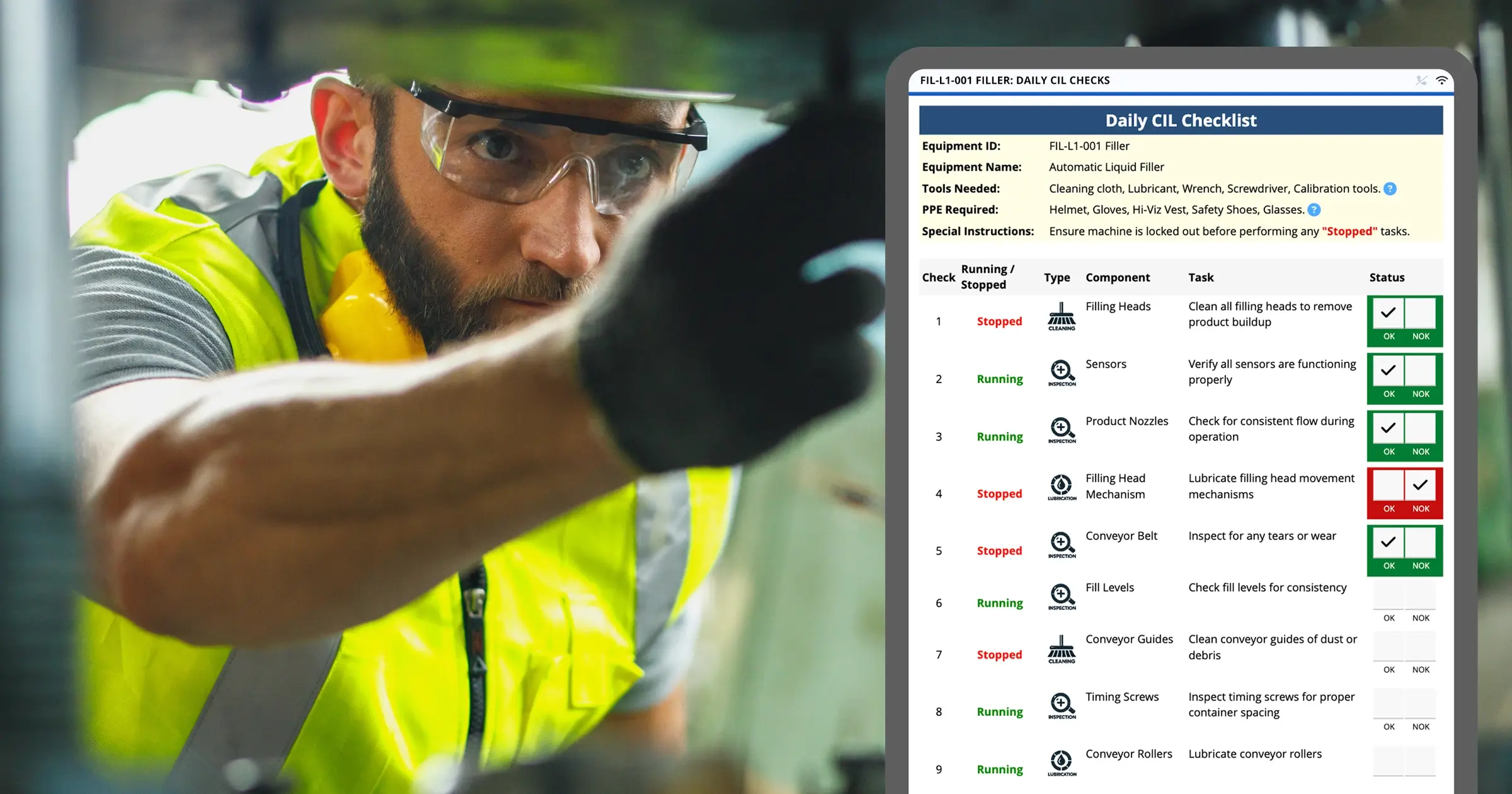
So what I want to do now is talk about consumer AI, again, the example of ChatGPT compared to industrial AI. And in the case of today, I’m going to give some examples of manufacturing companies that are actually using this technology today. But when you think about industrial operations, you have to think quite a bit differently than how we might use Gemini or ChatGPT today. So I’m just going to walk through an example here. You have a frontline worker, an operator on a manufacturing floor, and their job every day is to operate the mixer. Okay? Part of their job is also to periodically do a clean, inspect, and lubricate on that piece of equipment, so it doesn’t go down or so that they can prevent failures from happening. So that’s a CIL. So now go back to the context that I started this conversation with. Let’s say you have a less experienced worker, maybe they are a novice worker.