Autonomous Maintenance
See how Augmentir can help you connect and empower your workers and transform your frontline operations.
Autonomous Maintenance
Autonomous maintenance is a manufacturing strategy that places the responsibility for basic maintenance upkeep on the primary equipment user: the machine operator. It’s meant to prevent equipment deterioration by keeping it in like new condition.
Implementing autonomous maintenance provides operators with a greater sense of ownership and control of the equipment they use every day. They are in charge of completing basic maintenance activities like lubrication, cleaning and safety checks, which frees maintenance technicians to focus on more demanding tasks.
If you want to learn more about autonomous maintenance, read on as we discuss the following topics:
Autonomous maintenance is an approach to equipment maintenance that involves giving machine operators responsibility for basic upkeep tasks. This allows dedicated maintenance technicians to focus on more complex maintenance tasks.
This strategy is a pillar of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) an approach designed to optimize equipment performance and a foundational aspect of any lean manufacturing environment.
Employees using equipment daily are in the best position to continually monitor it and, with training, to keep it in top working order.
Autonomous maintenance (AM) gives operators more control over cleaning, lubricating, and inspecting their own equipment. They can also identify equipment issues early on before they become failures.
Successful AM requires that manufacturers provide their operators with the appropriate digital tools and knowledge to perform these tasks independently.
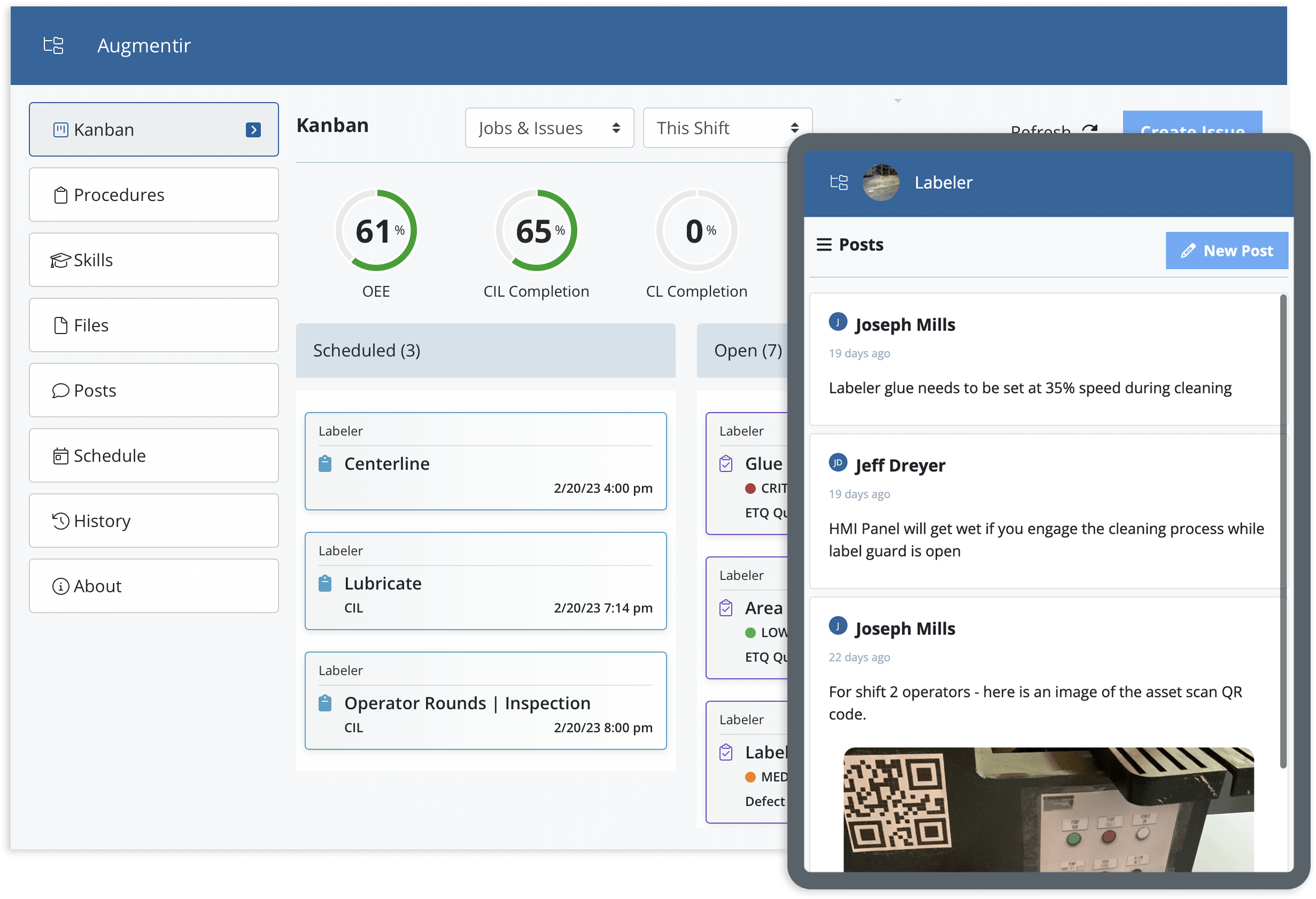
This involves digitizing standard operating procedures (SOPs) for cleaning, inspecting, and lubricating (CILs) and other ongoing preventive maintenance routines. Operators must also have easy access to training and a knowledge base of information. Real-time reporting with frontline operations platforms can help improve visibility and tracking for standard work:
The primary benefits of autonomous maintenance are:
These benefits help maximize equipment effectiveness and improve overall productivity. Learn more about the benefits of autonomous maintenance in our in-depth article, or read on to learn how to implement Autonomous Maintenance and why connected worker platforms are essential for successful autonomous maintenance.
See how Augmentir can help you connect and empower your workers and transform your frontline operations.
Implementing autonomous maintenance can be achieved through the following seven steps:
Use modern digital tools to train and guide operators to perform maintenance tasks and learn about the machines themselves. Connected worker platforms that incorporate digital work instructions and on-the-job training, including one-point lessons, enable operators to be successful at regular maintenance tasks.
This step involves the operator performing initial cleaning, inspecting, and resolving any equipment issues in need of repair. Standardized work instructions and digitized checklists provide accurate step-by-step guidance for operators to perform regular cleaning and repair activities.
During normal cleaning and inspection processes, operators should look at where contamination is coming from, and either remove or minimize the sources. For operators that are connected with digital tools, this represents a great opportunity to capture these activities and record them into a knowledge base for future operations.
Defining what operators will clean, lubricate, tighten and inspect, how they will do it, and how often the activities should be performed will help ensure that the equipment remains operational and in peak condition. In modern manufacturing environments, these standards are digitally captured into electronic SOPs and maintenance procedures.
Once operators are trained and have access to digital information to help guide them through the maintenance processes, they are able to perform cleaning, inspection, and lubrication (CIL) and preventative maintenance tasks independently and at an optimal level of safety and quality.
Manufacturers must also organize the workspace to make it easier for operators to complete maintenance tasks. The most useful tools include visual aids that reinforce standards and help operators understand the equipment, labeling, and how fluids should flow within the machine. These can be delivered to operators through digitized, visual instructions, which may include images or video guidance on equipment operation.
As operators become more digitally connected, manufacturers will have access to a rich source of data on how operators perform tasks. Through the use of artificial intelligence tools, data analytics, and operator feedback, manufacturers can gain insights into areas where the largest continuous improvement opportunities exist in productivity, training, workforce development, and content creation.
Once implemented, you can take several steps to improve your autonomous maintenance program.
Connected worker platforms are digital software tools that can help standardize and improve the way operators perform maintenance tasks. They are used to improve communication, collaboration, guidance, and support for the operators.
Connected worker platforms are also used to create, assign, and manage the maintenance tasks being done. Through a combination of digital work instructions and real-time collaboration tools, operators can independently complete maintenance tasks at peak performance.
Autonomous maintenance programs that leverage a connected worker platform provide value throughout the entire operation:
Furthermore, connected worker solutions that are built on an AI foundation are being used to support continuous improvement and lean initiatives in the workplace. AI-based connected worker solutions like Augmentir help focus continuous improvement teams on workforce productivity and work processes to reduce waste and bring value to the customer. Solutions like Augmentir are essential for digitizing an autonomous maintenance program and support a broader operational excellence strategy within the context of integrated work systems.
Manufacturing companies can provide operators with contextual information so they can perform their jobs at peak efficiency and solve problems faster.
This also allows organizations to capture valuable data not just on the work that is being performed, but also on how those workers are performing their jobs and what activities or interactions are contributing to the success or performance of certain jobs.
Interested in learning how Augmentir’s connected worker solution can help you implement autonomous maintenance within your manufacturing operation? Get in touch with us for a free demo.
See how Augmentir can help you connect and empower your workers and transform your frontline operations.
