Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing represents a significant shift from traditional manufacturing approaches, focusing on interconnectivity, data-driven decision-making, and worker augmentation with artificial intelligence (AI) and other digital technologies to create more efficient, flexible, and responsive production operations.
Today, manufacturing leaders use smart technologies and methods to increase sustainability and safety, improve asset and worker efficiency, enhance product quality, and reduce production costs.
To learn more about smart manufacturing, its benefits, examples of how it’s being used today, and how to enable it in your operations, read the guide below covering:
What is smart manufacturing?
Smart manufacturing was first mentioned in 2006, initially as ‘Smart Process Manufacturing’, at a National Science Foundation workshop on cyberinfrastructure.
It has since evolved to mean the application of advanced technologies and data analytics to improve manufacturing processes, making them more efficient, flexible, and sustainable. It leverages innovations such as connected worker platforms, artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and big data analytics to create connected production environments.
Today, smart manufacturing technologies and processes permeate many aspects of manufacturing from healthcare to building materials, using data and tools to optimize, reduce waste, and improve safety.
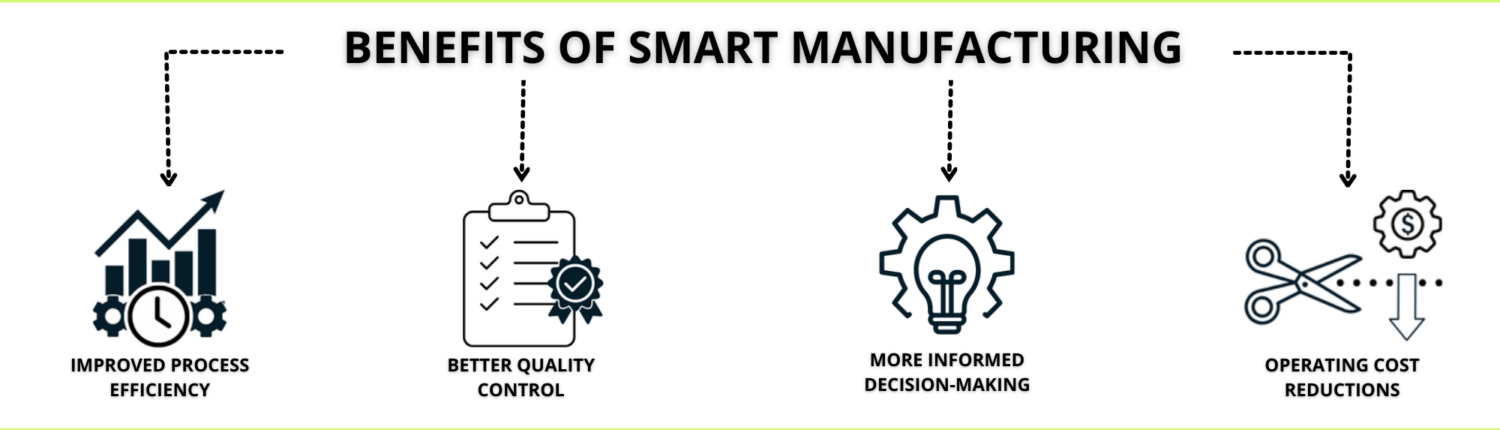
Benefits of smart manufacturing
Continuing economic uncertainties, constrained labor markets, and rising costs pose ongoing challenges for manufacturers, underscoring the importance of leveraging innovative technologies to improve manufacturing processes, enhance quality control, reduce operating costs, and allow frontline workers instant access to critical information for informed rapid decision-making.
- Improved Process Efficiency: Using advanced AI tools and connected technology manufacturers can make processes more efficient, improving asset efficiency by 20% on average. These tools can also predict equipment maintenance needs, optimize resource usage, and continuously monitor frontline activities to allow for immediate adjustments.
- Better Quality Control: Smart manufacturing initiatives enabled manufacturers to increase product quality by more than 30%. Connected quality solutions provide a closed-loop quality management ecosystem enabling smart manufacturing initiatives to break down silos and automate valuable factory-floor data mitigating the impact of poor quality while driving continuous improvement.
- More Informed Decision-Making: Innovative technologies allow frontline workers instant access to critical information in the flow of work, helping them make informed decisions quickly and efficiently. Furthermore, connected systems gather vast amounts of data from various sources within manufacturing processes, providing a comprehensive view of operations for management to create informed strategies and intelligent resource allocation.
- Operating Cost Reduction: Smart systems and advanced analytics ensure optimal use of resources minimizing waste and reducing material costs by 30% or more. Connected scheduling and other human capital management systems allow for smart staffing and labor forecasting so manufacturers can strategically upskill, reskill, and attract talent as needed. Lastly, predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring reduce unplanned downtime avoiding costly disruptions.
In addition to the above benefits, Deloitte studies recently found that smart factory initiatives increase worker safety and sustainability by more than 10%, creating a safer and more sustainable workplace for all.
Examples of smart manufacturing technologies
While many of the smart manufacturing activities began in Germany, today, these initiatives happen all around the world contributing to better, safer, and more sustainable manufacturing practices.
At its core, smart manufacturing is a technology-driven approach that uses interconnected systems and connected machinery to support and augment manufacturing workers, as well as optimize and improve manufacturing production processes.
Examples of smart manufacturing technologies in the industrial workplace include:
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connecting machines and devices to the internet to collect and exchange data, enabling real-time monitoring and control of manufacturing processes.
- Cloud Computing: Utilizing cloud-based platforms to store, manage, and process data, enabling scalable and flexible manufacturing operations.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Creating objects by adding material layer by layer, allowing for complex designs, customization, and rapid prototyping.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: Implementing AI algorithms to analyze data, predict maintenance needs, optimize production schedules, and improve decision-making processes.
- Big Data Analytics: Analyzing large volumes of data from various sources to gain insights, improve quality, reduce downtime, and enhance overall productivity.
- Augmented Reality: Using Augmented Reality (AR) for training, maintenance, and remote assistance, as well as for visualizing and simulating manufacturing processes.
- Digital Twins: Creating a digital replica of physical assets, processes, and systems to simulate, predict, and optimize performance.
- Industrial Robotics: Using robots for tasks like assembly, welding, painting, and material handling to increase precision, efficiency, and safety.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Robots designed to work alongside humans, enhancing productivity and safety by sharing tasks and assisting with complex operations. This is now being extended to include Generative AI assistants.
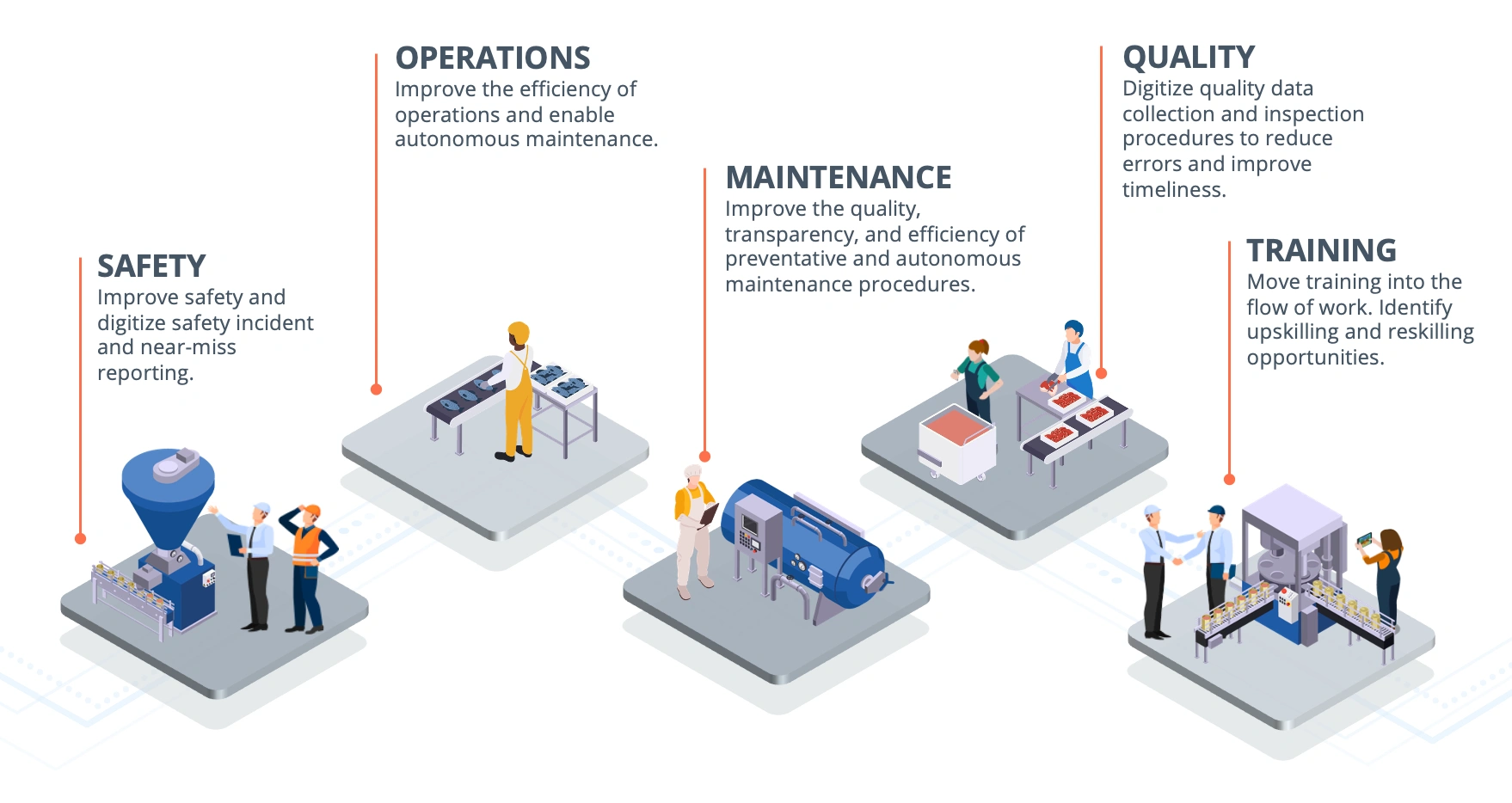
- Connected Worker Platforms: Leveraging mobile and wearable technologies to provide workers with real-time information, communication, and collaboration tools, improving safety, productivity, and decision-making on the factory floor. Connected worker platforms include digital work instructions, digital skills management and training, as well as tools to support use cases including connected safety, preventative and autonomous maintenance, connected quality, and shop floor training solutions.
These examples highlight the versatility and breadth of intelligent connected manufacturing tools, showcasing their ability to improve any aspect of the manufacturing processes in any industry.
Enable smart manufacturing with AI-Driven Connected Worker Technology
Continuing to embrace new technology and digital transformation is critical for manufacturers as they look for ways to capture unique opportunities and tackle the challenges they face. Approaches that leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and connected worker technology help to digitize manufacturing processes and uncover continuous improvement opportunities for improved worker efficiency and effectiveness.
AI-driven connected worker platforms are uniquely situated to help manufacturers reach various operational, workforce, and sustainability goals. This technology is poised to streamline manufacturing processes, prioritize frontline worker well-being, and contribute to the development of a fully integrated and connected manufacturing enterprise.
Implement Smart Manufacturing with connected worker tools from Augmentir
Augmentir is the world’s only Smart Connected Worker software suite that helps industrial companies implement smart manufacturing and optimize the safety, quality, and productivity of the industrial frontline workforce.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is smart manufacturing?
Smart manufacturing is the use of advanced technologies—such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), and cloud computing—to optimize manufacturing operations. It enables real-time data collection, predictive maintenance, and process automation to improve efficiency, quality, and agility.
How does smart manufacturing benefit manufacturers?
Smart manufacturing helps manufacturers reduce downtime, improve product quality, increase operational efficiency, and respond quickly to changing market demands. It enables data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement across the factory floor.
What technologies are used in smart manufacturing?
Smart manufacturing leverages technologies like AI, machine learning, digital twins, connected worker platforms, IIoT sensors, robotics, and edge/cloud computing. These tools work together to automate processes and provide real-time insights.
How is smart manufacturing different from traditional manufacturing?
Traditional manufacturing relies heavily on manual processes and siloed data, while smart manufacturing connects people, machines, and systems through digital technology. This integration enables real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and greater flexibility.
What role does AI play in smart manufacturing?
AI in smart manufacturing is used for predictive maintenance, quality control, process optimization, and workforce augmentation. It enables manufacturers to analyze vast amounts of data to uncover insights, automate decisions, and support frontline workers.
What is Augmentir’s role in smart manufacturing?
Augmentir provides an AI-powered connected worker platform that supports smart manufacturing by digitizing workflows, capturing tribal knowledge, and enabling continuous workforce development. Augmentir helps manufacturers improve productivity, reduce errors, and adapt to changing workforce dynamics.
How does smart manufacturing improve workforce productivity?
By using digital tools like connected worker platforms, smart manufacturing provides employees with real-time guidance, just-in-time training, and data-driven support. This reduces mistakes, shortens onboarding, and enables workers to perform tasks more efficiently and consistently.