Augmentir and UKG are working together to create a digitally connected frontline workforce that is shaping the future of work in manufacturing.
In manufacturing, success isn’t just about machines—it’s about people. But here’s the problem: workforce skills tracking and daily work execution have been handled separately for too long. The result? Misassigned tasks, skills gaps, slower production, and higher error rates.
The solution? Modernizing workforce management by digitally connecting frontline workers with AI-powered skills management and connected worker technology.
Together, Augmentir and UKG are delivering this solution to manufacturing companies around the world. Read on to discover how Augmentir and UKG are working together to create more productive, more engaged workforces in manufacturing.
Workforce Management for Modern Manufacturing Operations
Think of it like peanut butter and jelly: great on their own, but unstoppable together. When manufacturers sync traditional workforce management with AI-powered connected worker technology, they unlock huge benefits:
UKG’s leading workforce management solution, combined with Augmentir’s AI-powered connected worker platform empowers manufacturing companies to optimize labor efficiency, streamline scheduling, reduce mistakes, and ensure compliance, all while boosting productivity on the production floor.
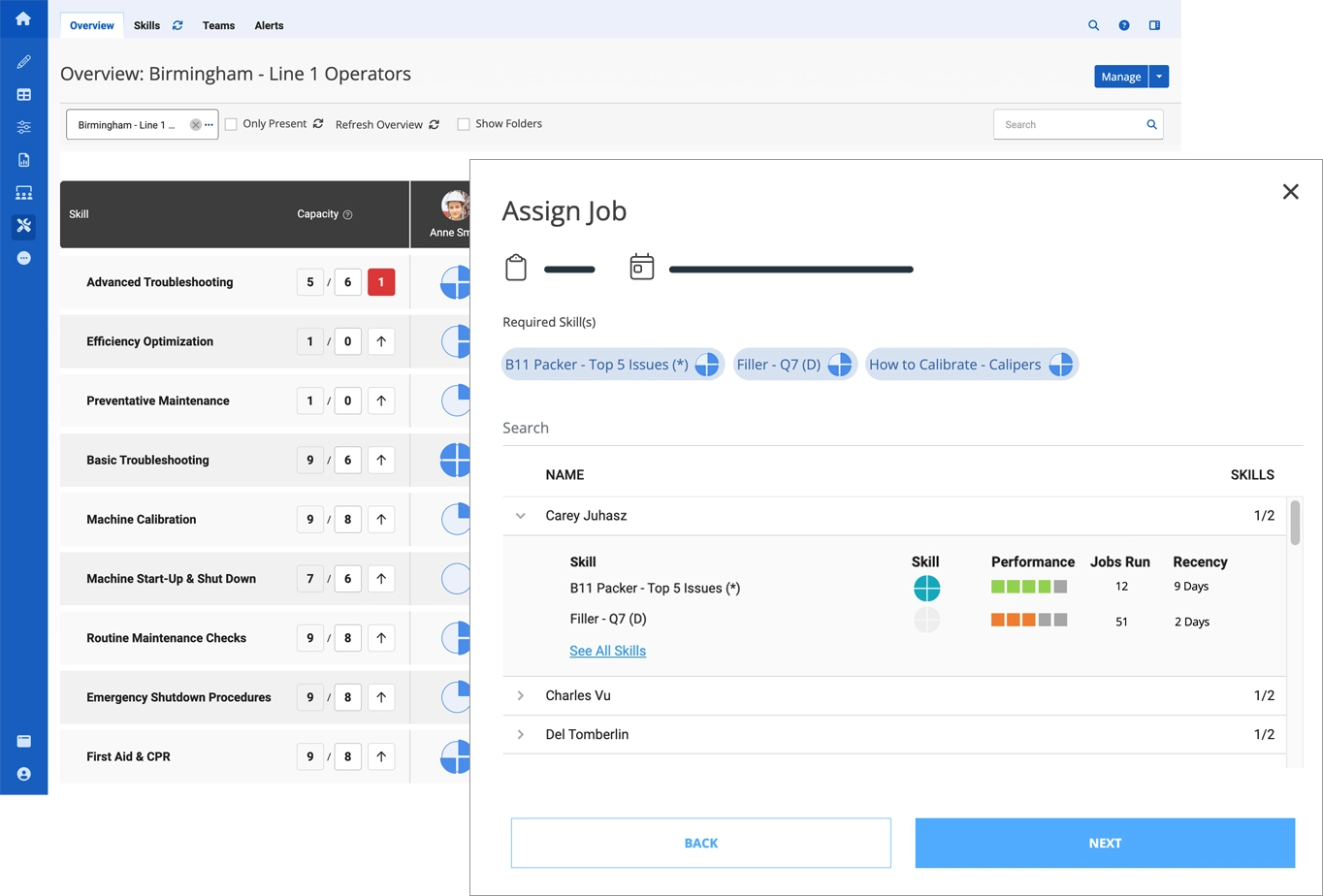
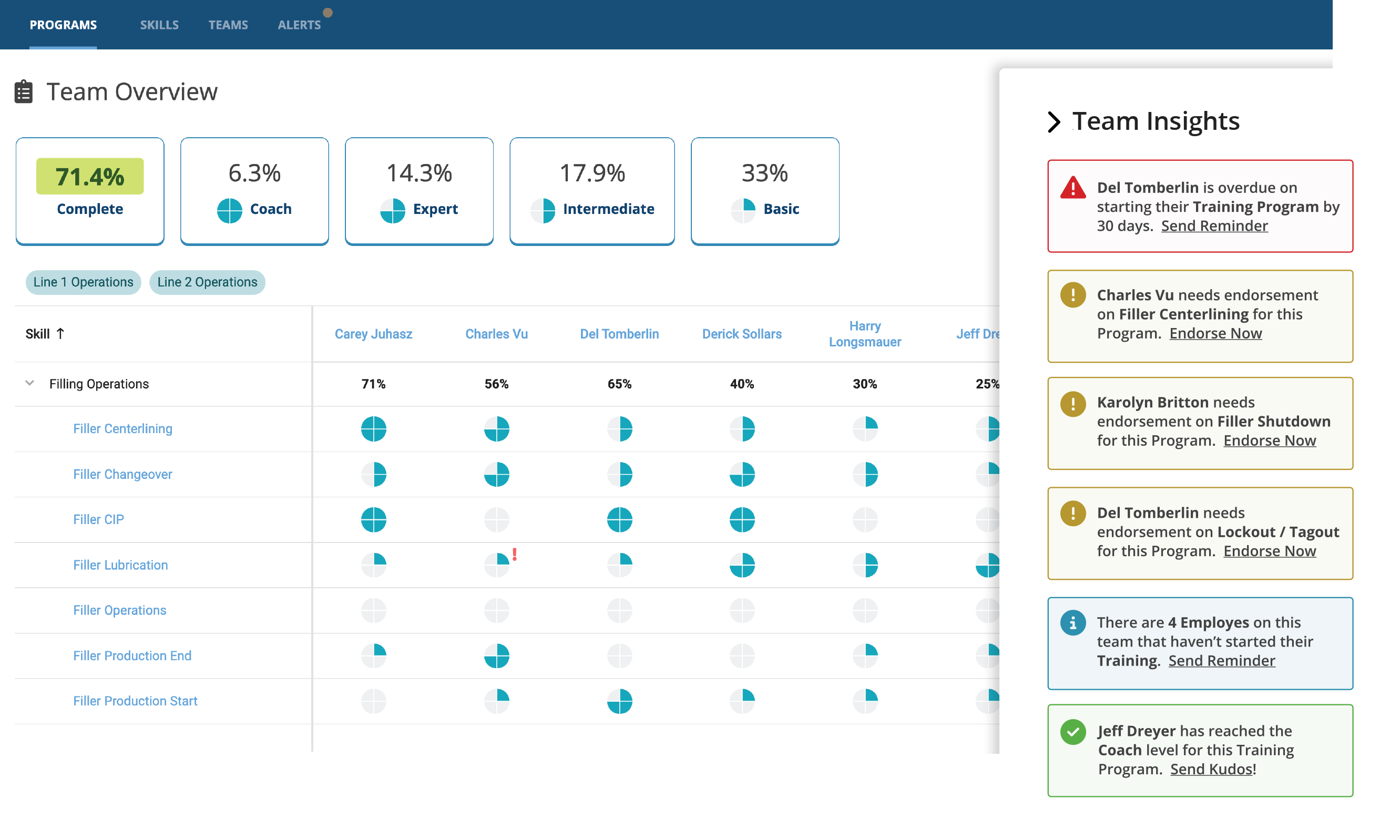
Manufacturing organizations that utilize both Augmentir and UKG Pro Workforce Management™ can benefit from connecting time and attendance, scheduling, and workforce data with Augmentir’s connected worker platform. Through this new integration, manufacturers can gain visibility into real-time, accurate employee information and skills tracking combined with AI-driven insights into work performance. By doing so, manufacturers can improve workforce efficiency and productivity and deliver more impactful training and support for frontline workers.
- Right worker, right job – Workers are assigned tasks based on real-time skill assessments.
- Training in the flow of work – No need to step away from production; learning happens in real time
- Faster onboarding – New hires get up to speed quicker with AI-driven, step-by-step guidance.
- Fewer mistakes, higher efficiency – Workers get exactly the information they need, when they need it.
- Continuous upskilling – As employees complete tasks, their skills profiles automatically update.
- Smarter capacity planning – Give production teams improved capacity planning and a better decision support tool for daily workforce scheduling and management. Proactively look ahead and see coverage gaps based on employee scheduling.
Augmentir’s UKG connector streamlines the flow of employee data into Augmentir, providing operations leaders and plant managers with valuable insights into worker availability, productivity, training effectiveness, and more. This gives production teams improved capacity planning and a better decision support tool for daily workforce scheduling and management.
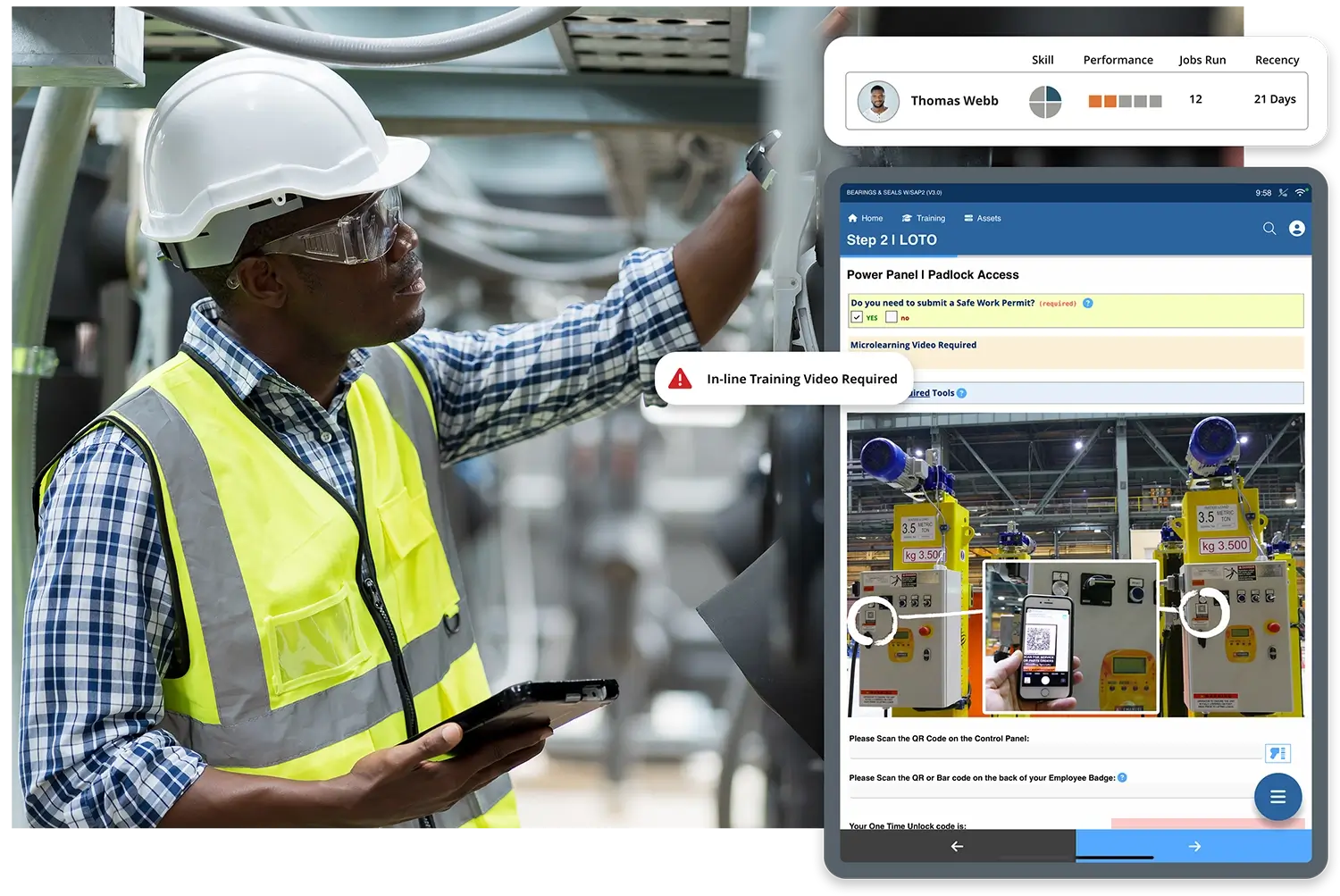
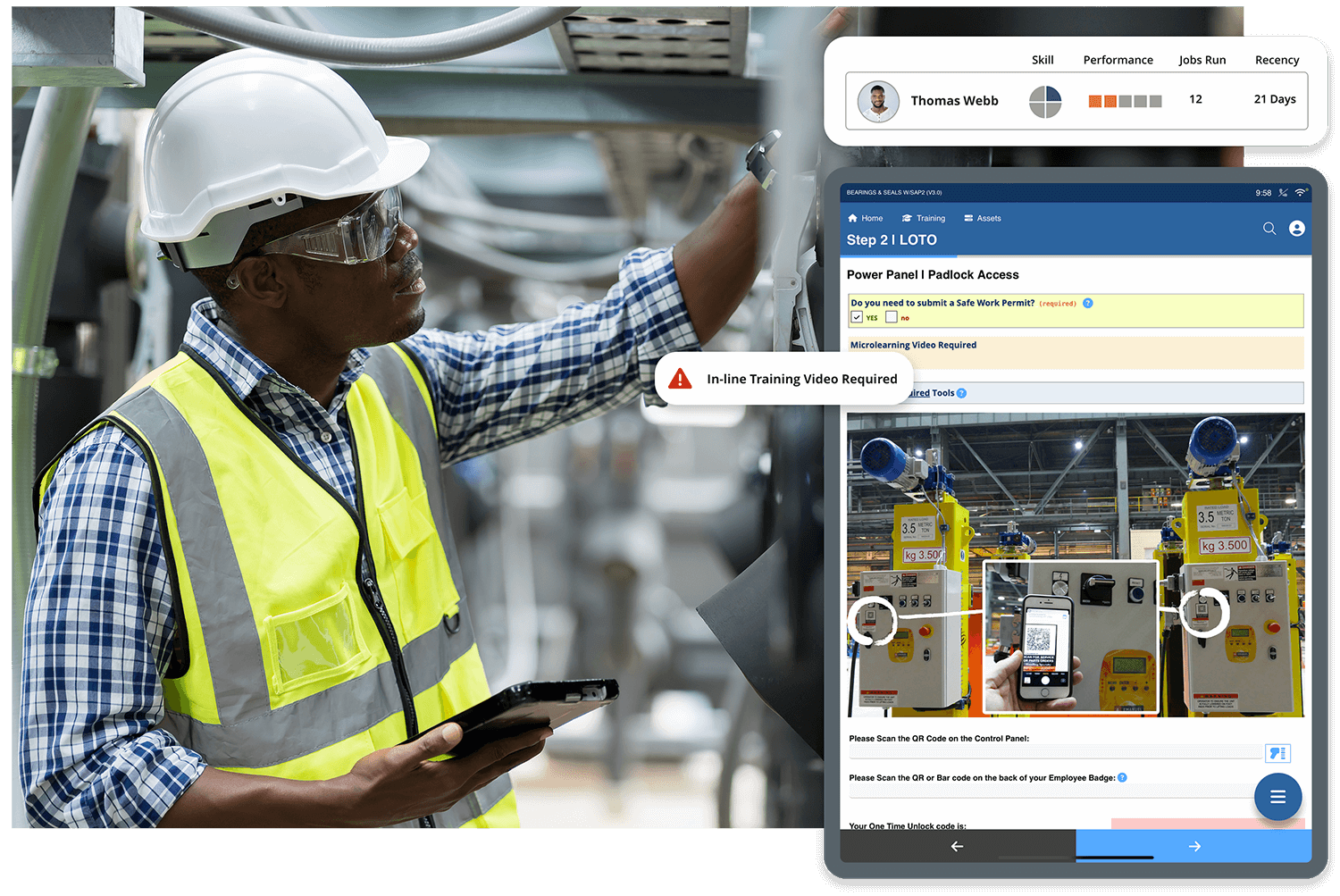
Gone are the days of outdated skills databases and generic training programs. Today, learning happens on the job, in the moment, and at the worker’s fingertips. Manufacturers can provide personalized on-the-job support to employees through Augmentir’s digital guidance, bringing training in the flow of work and alleviating potential skills gaps.
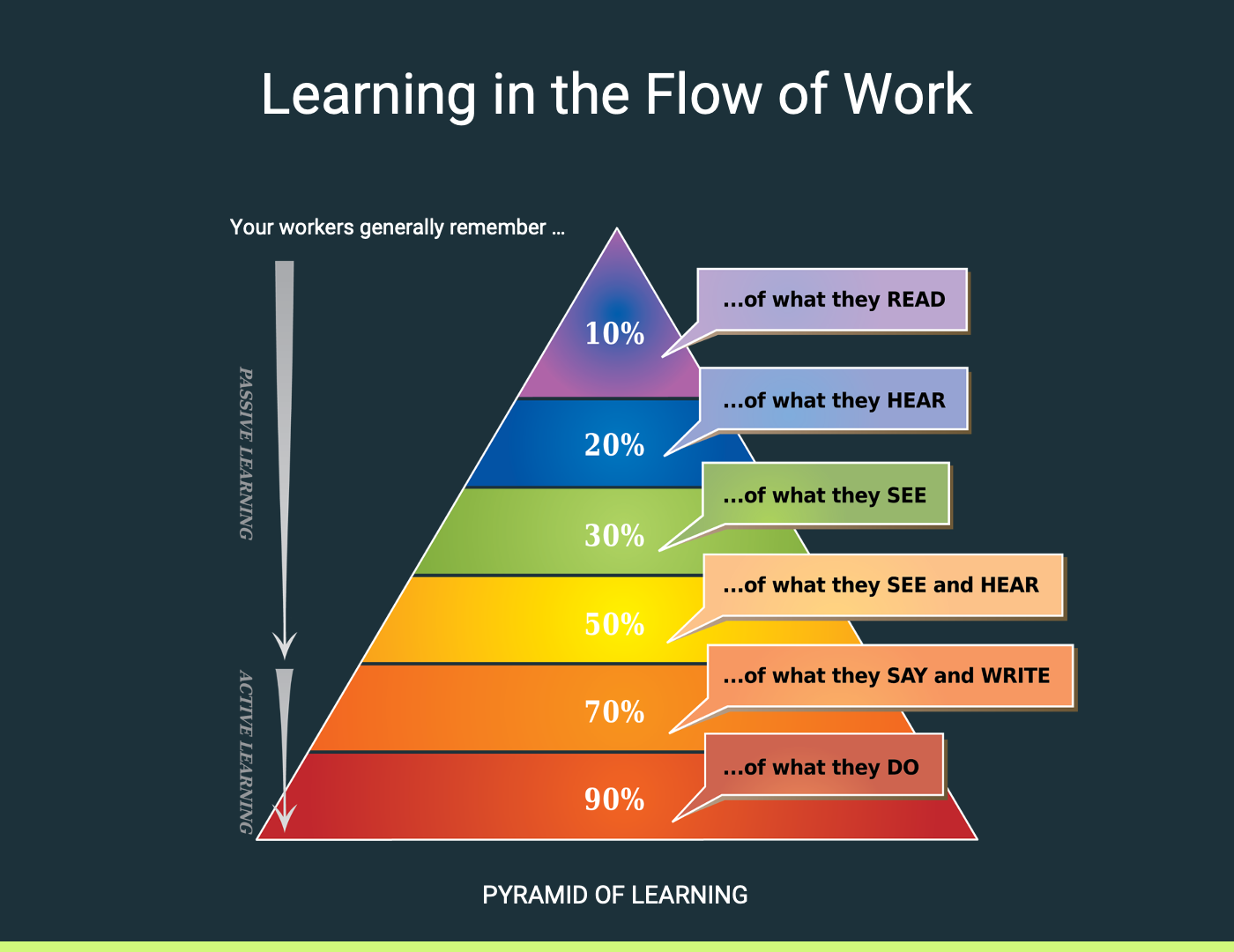
The Future of Training: Learning in the Flow of Work
Traditional workforce training methods are outdated. Long classroom sessions, dense manuals, and generic training modules don’t cut it anymore—especially in fast-paced manufacturing environments. Workers need real-time, task-specific guidance to build skills and stay productive.
That’s where embedded training comes in. Instead of separating learning from work, Augmentir enables:
- Just-in-time training – Employees learn exactly what they need, right when they need it.
- Mobile, interactive work instructions – Step-by-step guidance delivered on the shop floor.
- Skills-based task assignments – Workers are matched to jobs they’re qualified for, with training baked in.
- Continuous learning & upskilling – As workers complete tasks, their skills profiles evolve, keeping pace with job demands.
This approach not only accelerates onboarding but also reduces downtime, improves accuracy, and keeps workers engaged—all while production continues at full speed.
How Augmentir and UKG are Shaping the Future of Work in Manufacturing
Augmentir’s AI-powered connected worker platform makes skills integration effortless. By delivering smart, adaptive digital work instructions, Augmentir ensures that:
- Workers receive personalized guidance based on their experience level.
- Skills data stays fresh, automatically updating as tasks are completed.
- Training gaps are filled in real time, keeping production smooth and efficient.
- Supervisors have full visibility into workforce capabilities and gaps.
For manufacturers like Armstrong World Industries (AWI), this has been a game-changer. Facing workforce shortages and declining tenure rates, AWI needed a way to ensure workers had access to the right information at the right time. By adopting Augmentir, AWI empowered its frontline workers to operate equipment, troubleshoot issues, and execute tasks with confidence—all through a single, mobile interface.
The Power of the UKG + Augmentir Partnership
The digital transformation of today’s manufacturing workforce doesn’t stop with Augmentir alone. The partnership between UKG and Augmentir takes workforce optimization to the next level.
By combining UKG’s workforce data (scheduling, time tracking, and HR insights) with Augmentir’s AI-driven skills tracking and adaptive work instructions, companies can:
- Schedule workers smarter – Assign shifts based on real-time skill levels.
- Close skills gaps faster – Proactively upskill employees before gaps cause production delays.
- Improve retention & engagement – Give workers clear paths for career growth and skill development.
- Boost operational efficiency – Match the right person to the right job, every time.
This isn’t just about automation—it’s about empowering people. When employees have the skills, training, and resources they need in the flow of work, they stay longer, perform better, and drive business success.
Bottom Line? Augmentir + UKG = The Future of Work in Manufacturing
The manufacturers that integrate digital skills tracking with connected worker technology that supports daily operations will be the ones that thrive in an era of workforce disruption. Augmentir and UKG are making it happen – helping companies close skill gaps, improve efficiency, and build a workforce that’s future-ready.