Learn about autonomous and preventive maintenance, and how they can maximize machine efficiency and worker productivity on the shop floor.
Autonomous and preventive maintenance are two manufacturing strategies for maintaining machinery on the shop floor. The main difference between the two is that autonomous maintenance (AM) places greater responsibility for equipment upkeep on operators, while preventive maintenance (PM) is carried out by maintenance workers. Both autonomous and preventative maintenance strategies benefit from smart, connected worker technologies, although in different ways.
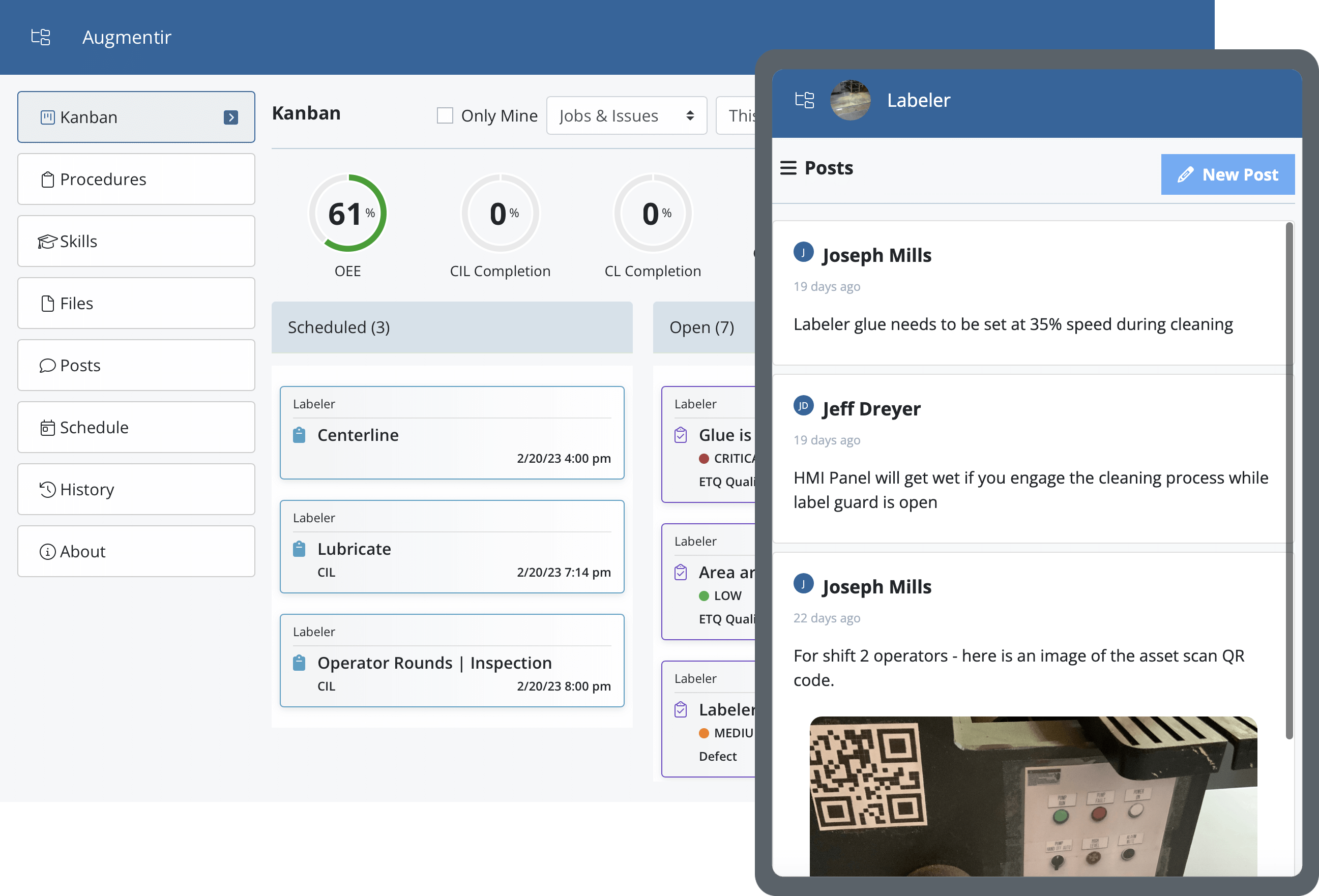
AM, for example, focuses on training machine operators to be the point of reference for cleaning, inspecting, and making minor repairs on the spot. This approach aims to empower operators to take the initiative in monitoring their equipment and identifying issues early on. By introducing smart, connected worker technology, like Augmentir’s suite of connected worker tools and closed-loop autonomous maintenance solution, manufacturing leaders can give operators more control over inspections and help intelligently guide and support operators, resulting in minimized machine downtime.
PM, on the other hand, consists of scheduling regular maintenance activities like part replacement, lubrication, and calibration. Workers tasked with PM ensure equipment remains in tip-top condition, which helps to prevent future breakdowns. The goals of this strategy are to avoid machine downtime and reduce the need for unplanned repairs. Smart, connected worker solutions improve the quality, transparency, and efficiency of both autonomous and preventive maintenance and repair procedures by standardizing and optimizing maintenance procedures.
You can learn more about autonomous and preventive maintenance by exploring the following sections:
- What’s autonomous maintenance and its advantages?
- What’s preventive maintenance and its benefits?
- How to implement AM
- How to implement PM
What’s autonomous maintenance and its advantages?
Autonomous maintenance involves machine operators tackling basic equipment upkeep tasks to ensure that everything runs smoothly on the production floor.
When implemented, AM can yield a number of benefits:
- Reduced equipment downtime: Conducting routine upkeep activities can prevent breakdowns and limit the need for unplanned maintenance.
- Greater machine reliability: Operators who are trained to maintain their own equipment are more likely to pinpoint problems before they lead to machine failure.
- Prolonged lifespan of machinery: Equipment that is maintained will last longer and require fewer repairs or replacements.
- More operator involvement: Operators who take an active role in preserving their machinery feel empowered.
- Increased safety: It’s easier to troubleshoot potential hazards before they turn into accidents when operators frequently inspect and maintain their equipment.
- Cost-effectiveness: Reducing unplanned maintenance can save manufacturers significant money over time.
When coupled with smart, connected worker technology and AI-driven analytics, AM’s benefits are further enhanced. Digitizing autonomous maintenance processes increases standard work adherence, clears defects faster, and improves auditability. Connected worker technology enables operators to share knowledge and gives them access to the resources they need right when they need them.
What’s preventive maintenance and its benefits?
Preventive maintenance focuses on performing routine equipment upkeep tasks at scheduled intervals. The goal is to avert equipment failure and limit unplanned downtime or repairs.
The benefits of having dedicated workers perform preventive maintenance are:
- Enhanced machine reliability: Regular maintenance increases the odds of identifying and fixing problems before they turn into mechanical failures.
- Decreased downtime: Conducting routine upkeep at scheduled times can decrease unplanned maintenance and increase production efficiency.
- Greater compliance: PM can help manufacturers better comply with regulatory requirements to prevent unnecessary penalties for non-compliance.
- Better planning protocols: Recruiting specialized maintenance personnel with extensive training on machine upkeep and repair can lead to better planning and allocation of resources.
- Increased safety: Training workers on basic maintenance techniques ensures that deficiencies are addressed in a timely manner to avoid any injury.
PM’s impact is improved when used alongside smart, connected worker solutions that allow for digital work instructions and remote collaboration to effectively and efficiently guide technicians. Additionally, by digitizing and automating maintenance notifications, organizations can improve communications, speed up maintenance procedures, and minimize machine downtime.
How to implement AM
Applying autonomous maintenance to everyday maintenance tasks can mitigate potential machine disasters. Organizations can take this even further by creating “smart” autonomous maintenance processes and implementing advanced connected worker solutions with AI-driven insights. This gives operators improved control over maintenence process and expert guidence through a searchable asset hierarchy, maintenance history, and troubleshooting database.
The seven steps of effective AM implementation:
- Boost operator expertise: It’s important to train operators on the machines themselves and how to perform maintenance tasks. This type of training can be made more effective through AI-based insights that integrate skills management into the flow of work and identify workforce development opportunities for upskilling and reskilling.
- Conduct initial cleaning, inspection, and repairs: Operators should execute regular maintenance activities to avoid unplanned downtime. Furthermore, with connected worker solutions, operators can use mobile devices to digitally track and manage issues and activities as well as automate maintenance notifications further reducing overall downtime and avoiding unplanned downtime.
- Eliminate causes of contamination: Routine cleaning and inspection minimize sources of contamination such as improper calibration and defective equipment. This alone can help prevent unexpected machine breakdowns. By building smart workflows into the autonomous maintenance process, manufacturers can schedule and assign standard work procedures (such as routine cleaning and calibration) digitally that have built-in work reporting for better visualization and auditing.
- Define standards for cleaning, lubricating, and inspecting: Nailing down how to clean, lubricate, tighten and inspect, and how often to perform these upkeep duties, can help keep equipment in pristine condition. Smart digitization can standardize these practices across all manufacturing operations, giving organizations a global best practices standard to measure standard work adherence, clear defects more quickly, and improve auditability.
- Perform inspection and monitoring: Operators who are trained on maintenance processes can carry out maintenance tasks independently and without error. With smart skills management and AI-enhanced workforce development, organizations can reduce training time and provide individualized guidance and support to workers when and where needed.
- Standardize visual maintenance: Incorporate visual aids that help operators better understand equipment and labeling. For example, written procedures could contain a diagram showing how fluids should flow in a particular machine. Continuous learning and personalized insights via connected worker solutions are able to take this one step further and integrate things like instructional videos, interactive diagrams, and even remote experts into the flow of work to improve operational excellence and productivity.
- Work towards continuous improvement: It’s imperative to strive for continuous improvement in maintaining machinery. Operators who are constantly learning and evolving are more productive and empowered with better decision-making capabilities through actionable, AI-driven insights.
Learn more on how to implement autonomous maintenance and the seven steps involved, or get in touch with us for a personalized demo to see Augmentir’s Autonomous Maintenance solution in action.
How to implement PM
According to Forbes, when implemented correctly, preventive maintenance ensures that upkeep is performed at a set time to prevent unexpected machine deficiencies. Smart, connected frontline worker solutions are able to improve preventative maintenance procedures through smart communication, scheduled notifications and improved collaboration.
Eight steps for implementing preventive maintenance:
- Establish project scope: Gauge which machinery will be inspected and which maintenance tasks are needed to be done at specific intervals.
- Pinpoint upkeep requirements: Set requirements for which tasks are crucial for each piece of equipment. Tasks could vary from lubrication and calibration to inspections and part replacements.
- Create maintenance schedule: Create a set schedule for carrying out PM tasks that’s based on equipment requirements, production schedules, and planned downtime.
- Allocate worker responsibilities: Assign which tasks each maintenance worker is expected to fulfill.
- Provide necessary resources: Give staff the proper tools, equipment, and supplies to execute PM tasks (e.g., lubricants, replacement parts, testing equipment, etc.).
- Define metrics: Establish metrics for gauging the efficiency of PM (e.g., downtime, equipment reliability, maintenance costs, etc.).
- Create training programs: Hands-on training and how-to instructions can help maintenance workers better understand how to perform upkeep tasks.
- Monitor performance and adjust: Measure how well your PM efforts are doing and revise if necessary. This may mean updating procedures, adjusting maintenance schedules, or creating more training opportunities.
All of these steps are able to be standardized and optimized through connected worker solutions. Augmentir’s suite of connected worker tools delivers in-line training and support at the point of work, provides a searchable database to allow workers access to knowledge when and where needed, gives workers individualized guidance and support, connects teams for better collaboration, and more. This approach helps standardize and optimize maintenance processes and notifications as well as training, offering a better, more efficient adoption process for both frontline workers and management from start to finish, and giving everyone the proper tools for successful manufacturing operations.
If you are interested in learning for yourself why companies are choosing Augmentir to help digitize and optimize their autonomous and preventive maintenance programs – reach out to book a demo.